Isotopes in Canada
What is a medical isotope?
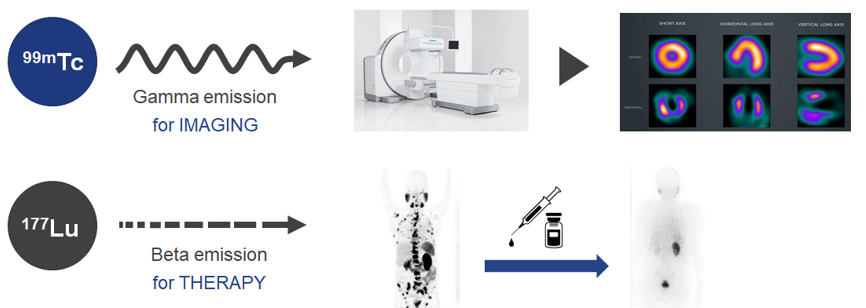
An isotope that emits radiation that is used to diagnose or treat disease
Isotopes are atoms that have the same number of protons as each other, but different numbers of neutrons. There are both stable and non-stable isotopes, of which the unstable forms exhibit characteristic radioactive decay via electromagnetic (gamma) or particulate (alpha, beta, Auger, etc.) emission.
What is half-life?
Each isotope also has its own unique “half-life”: the time it takes for half of the atoms to undergo radioactive decay. A radioactive half-life (t½) can range in duration from nanoseconds to hundreds of thousands of years.
How are isotopes produced?
Isotopes can be produced by both reactors and cyclotrons. These methods are complementary.
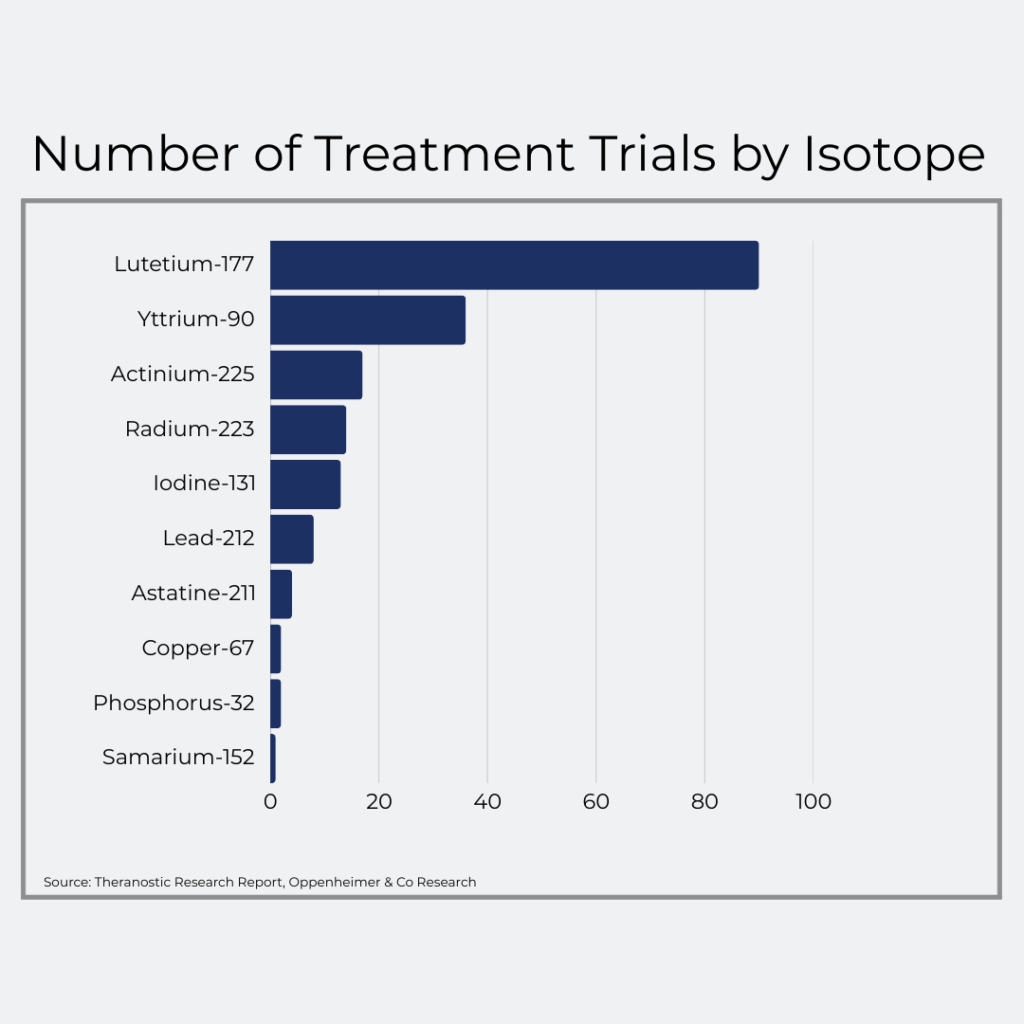
- Lutetium-177
- Molybdenum-99
- Cobalt-60
- Iodine-125
- Yttrium-90
- Iodine-131
- Radium-223
- Holmium-166
- Flourine-18
- Gallium-67
- Iodine-123
- Copper-64
- Copper-67
- Zirconium-89
- Indium-111
- Carbon-11
- Nitrogen-13

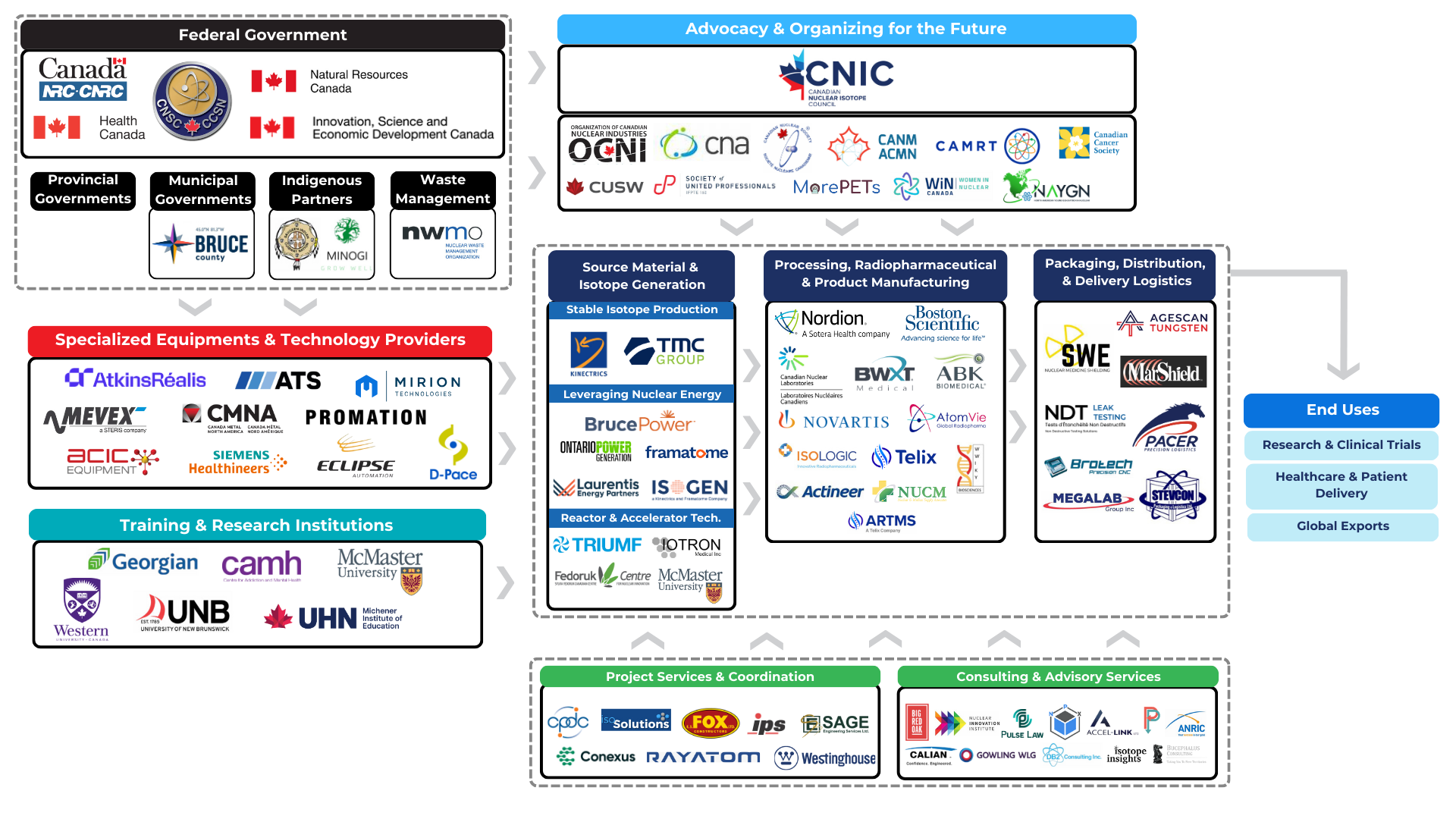
Medical Isotope Supply Chain
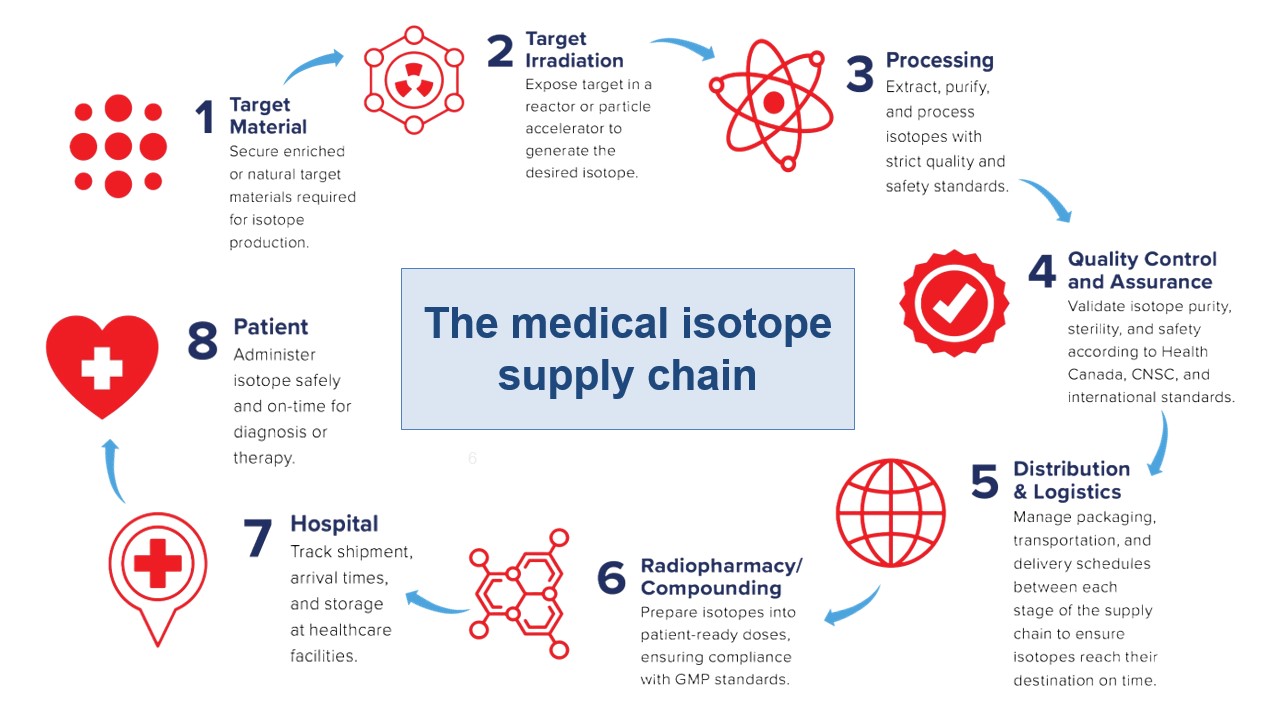
Canadian Isotope Supply Chain
The complete supply chain for the production, processing and delivery of medical isotopes is represented in Canada.
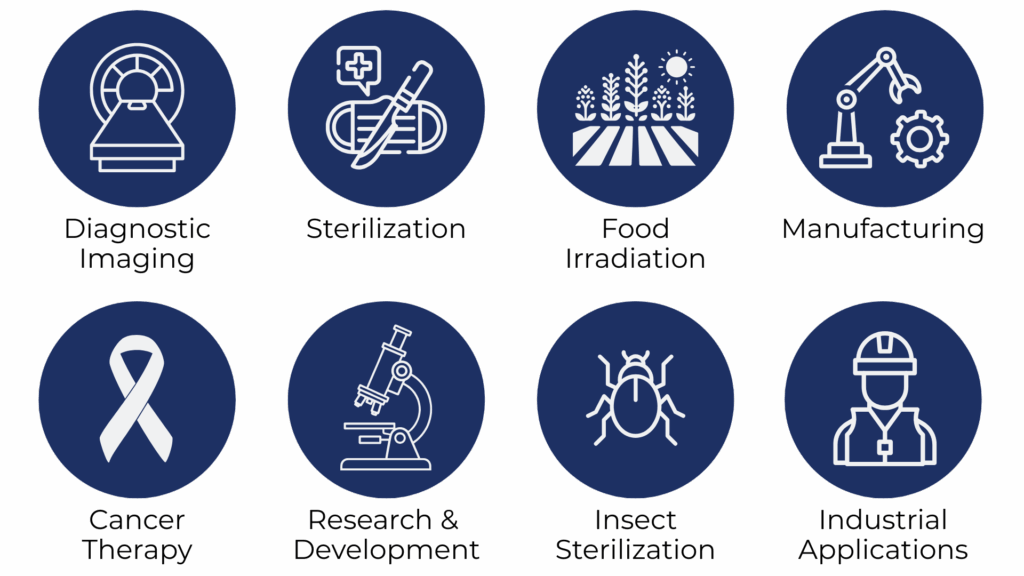
Applications of Isotopes
Strategic Priority for Canada
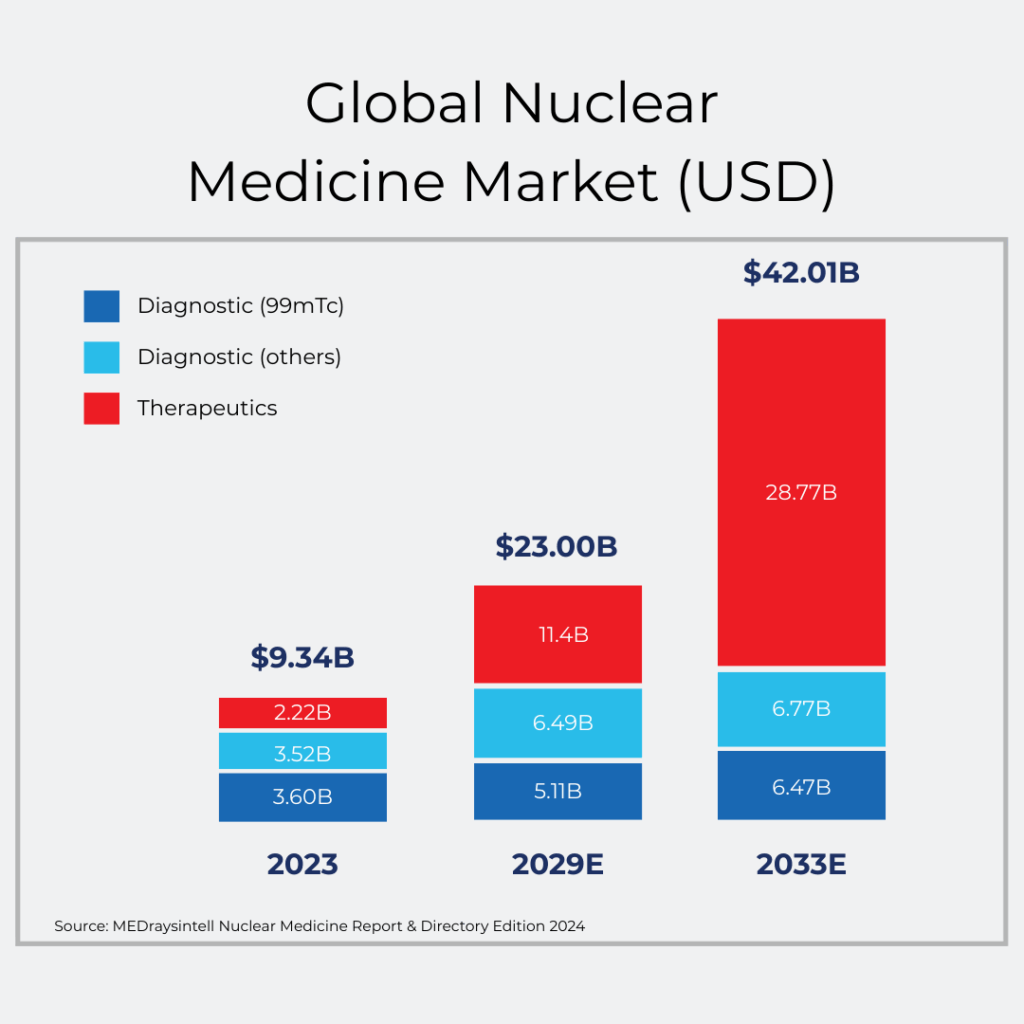
The global isotope market is rapidly growing, and Canada has an opportunity to expand its historic leadership within the sector. Governments across the country should identify isotopes as a strategic priority for Canada, seizing the opportunity for expansion and securing Canada’s continued global leadership in this space.